Description
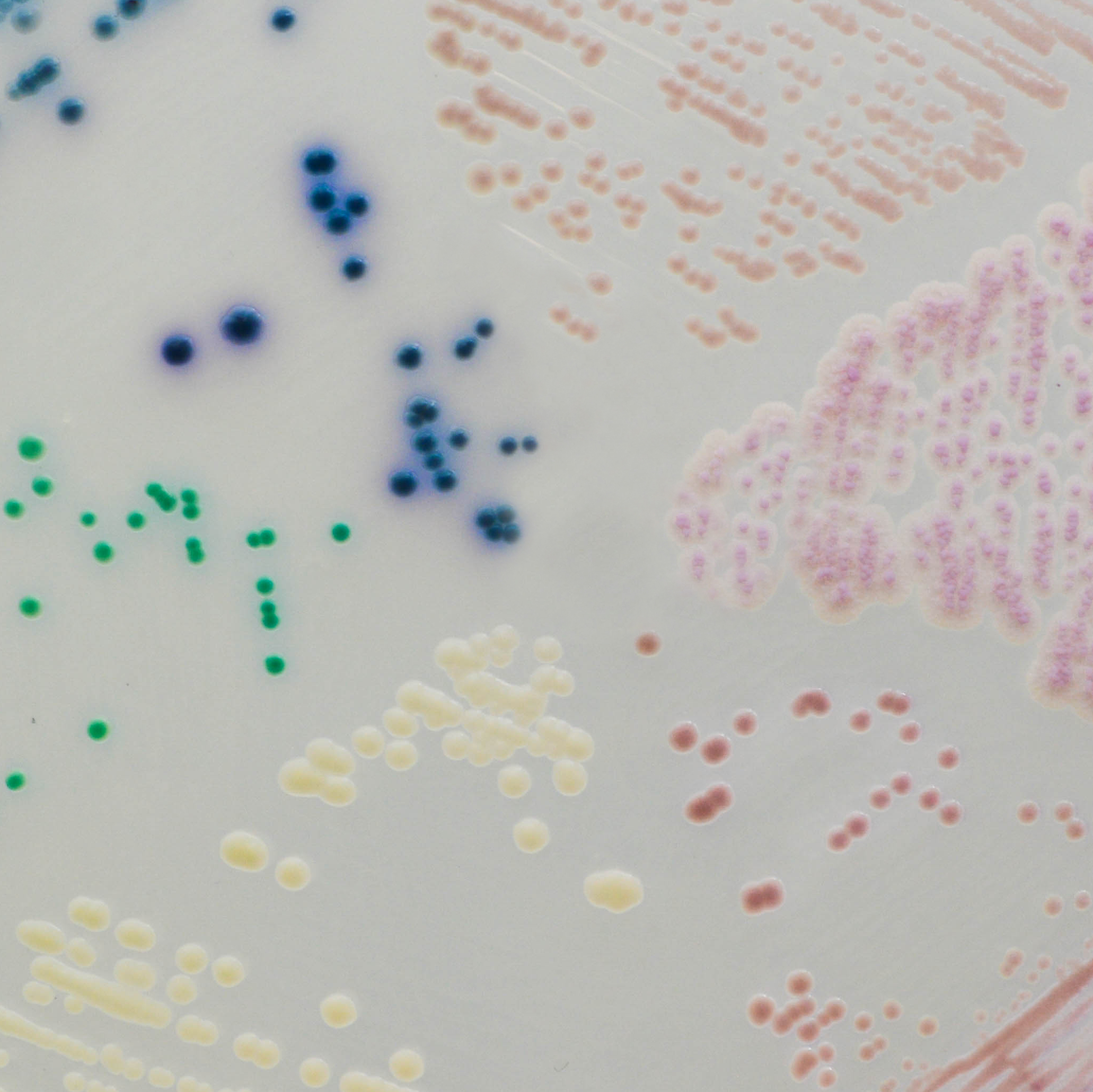
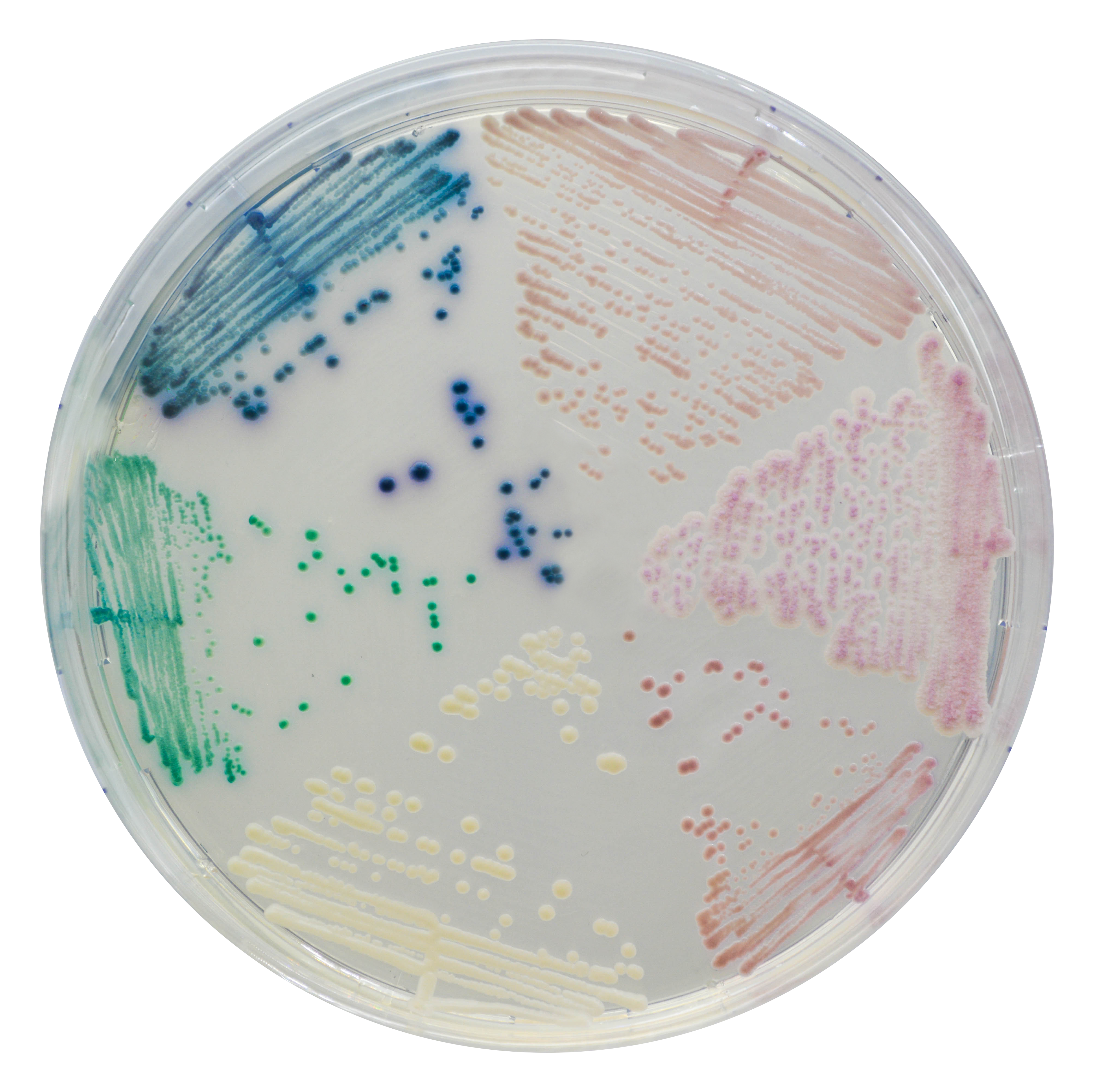
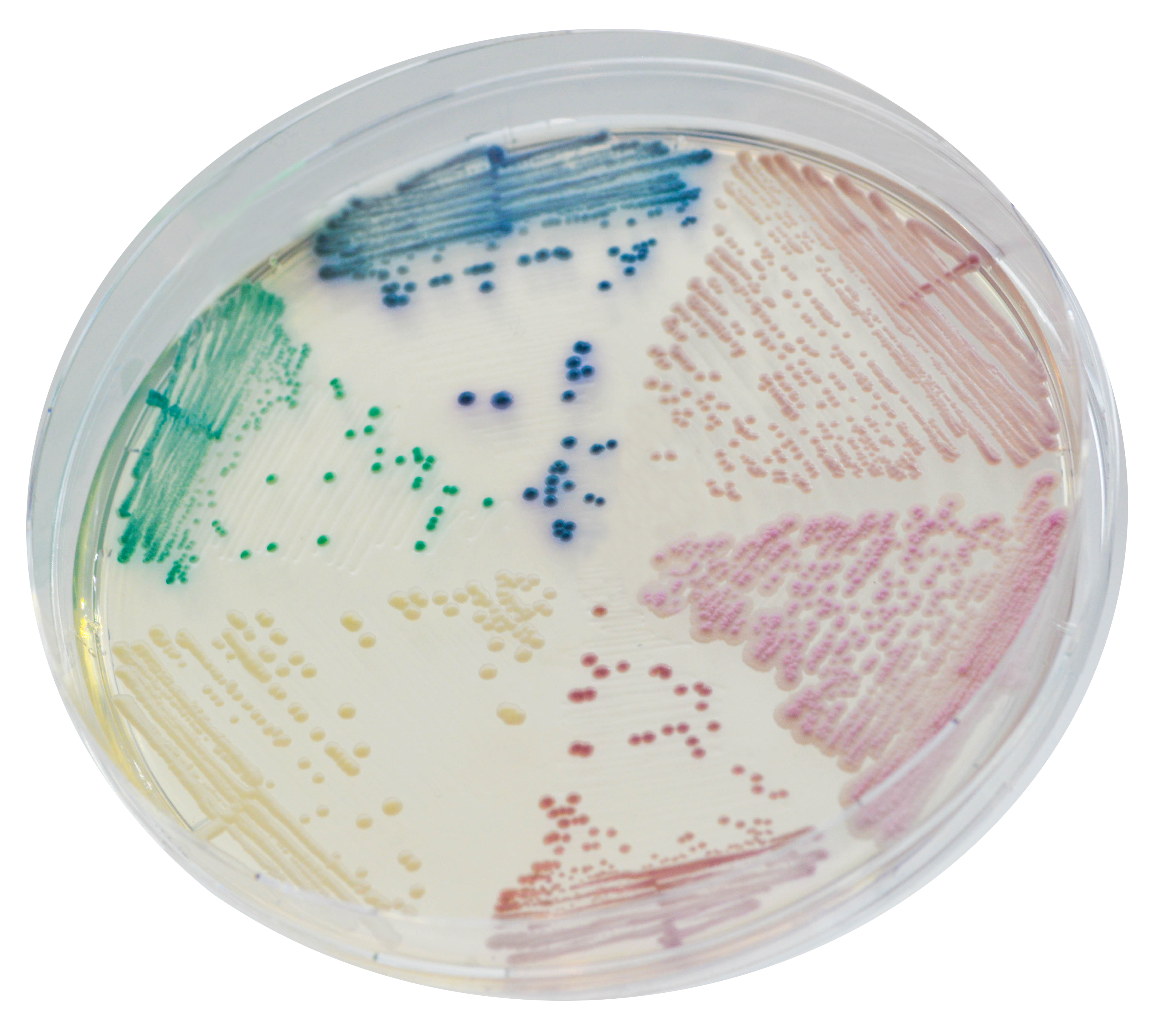
Apparence des colonies
Candida albicans
vert
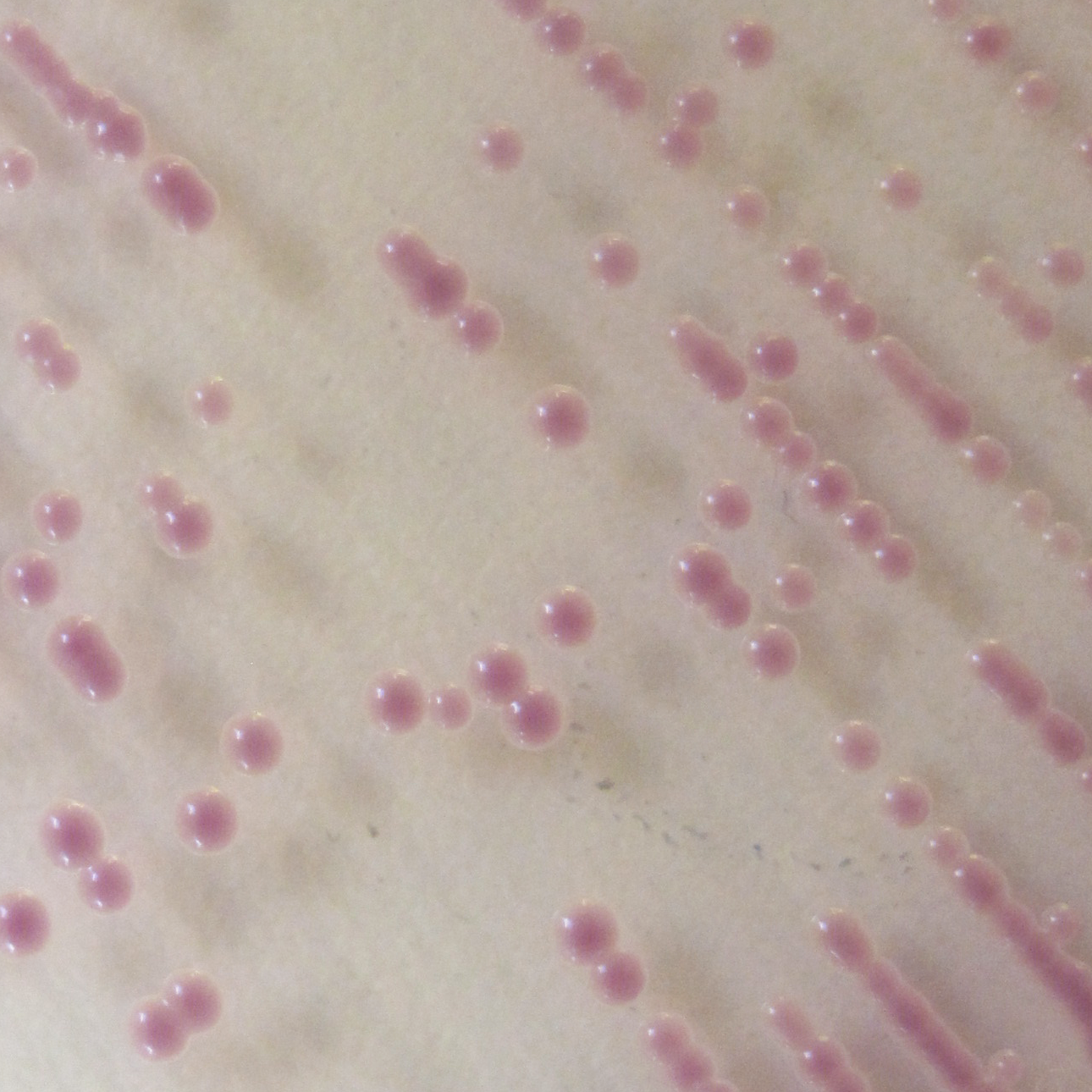
Candida glabrata
mauve
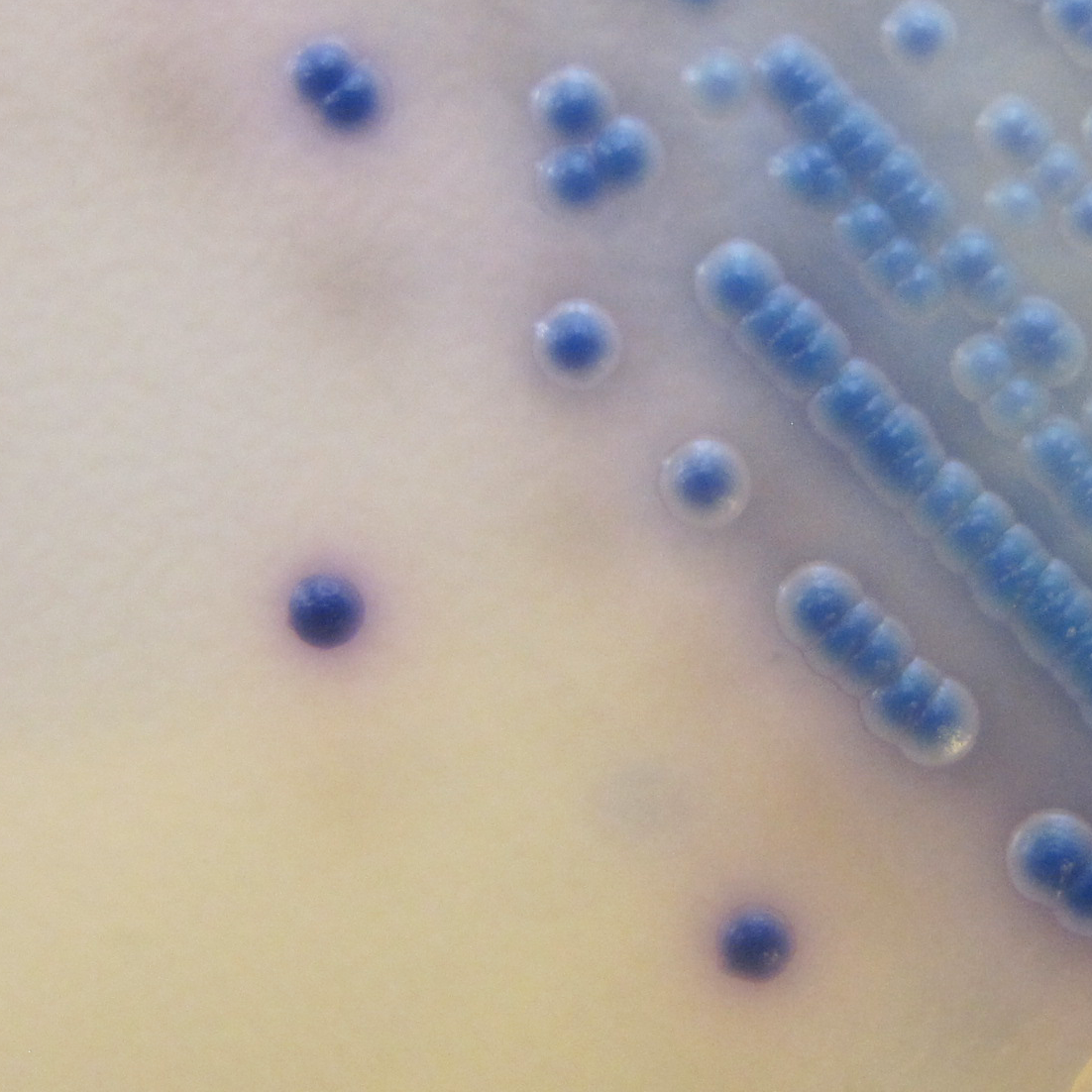
Candida tropicalis
bleu métallique
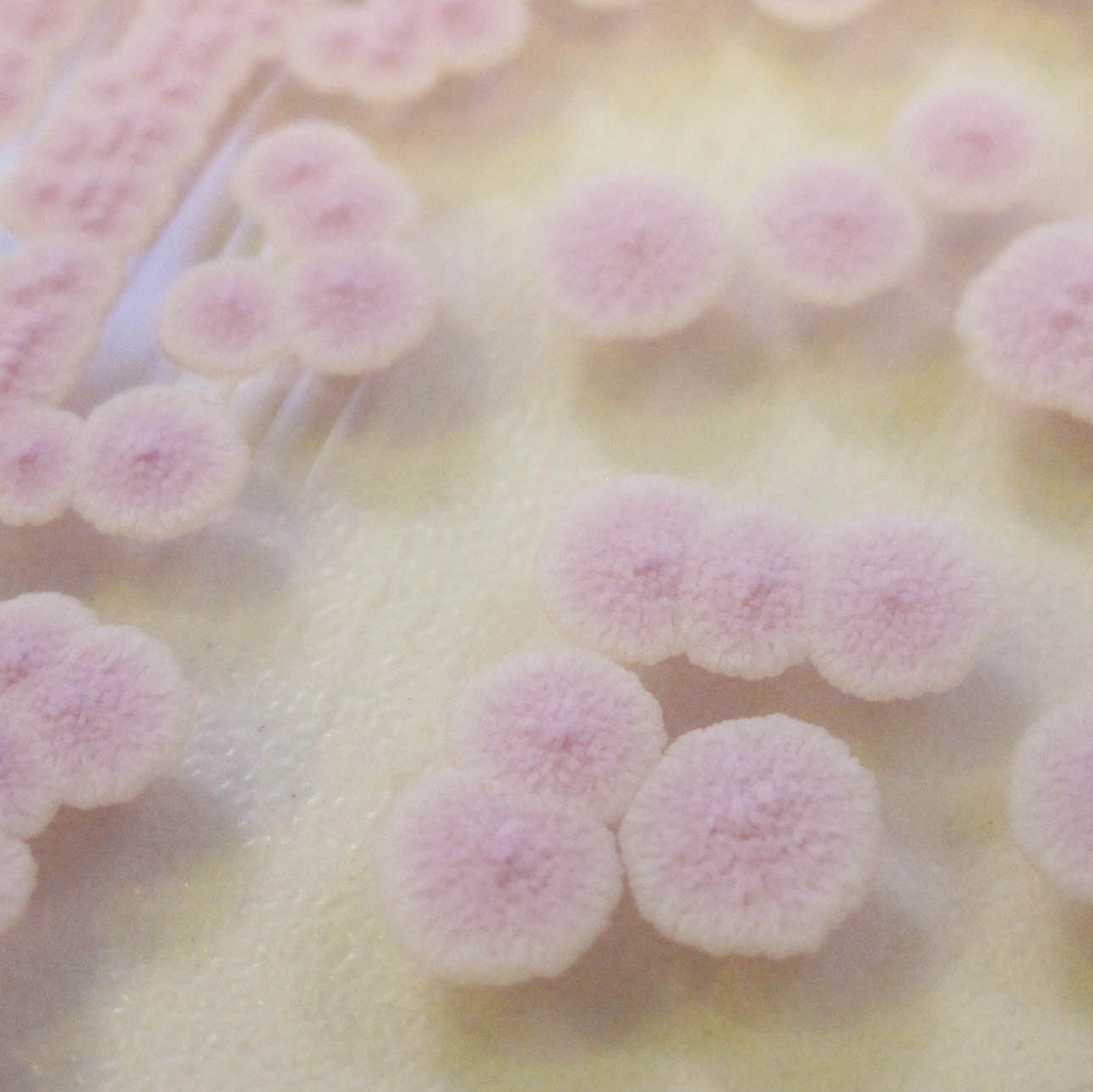

Candida krusei
rose, duveteux
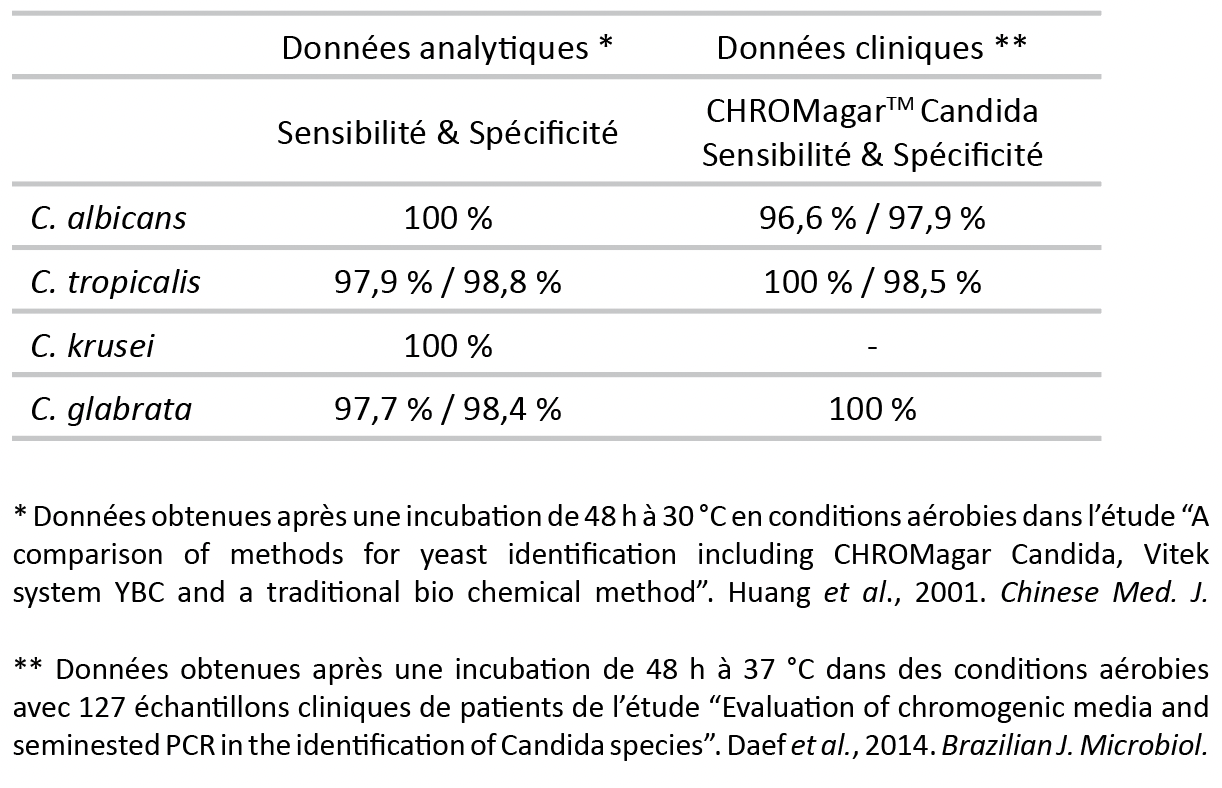
Performances
La diminution de la résistance des patients et l’augmentation du nombre d’hôtes sensibles résultant des progrès du traitement médical, font que les cas d’infections sanguines dû à Candida ont augmenté au cours des années 1990, pour finalement, se stabiliser ces dernières années. Le plus souvent, Candida est impliqué dans les infections oropharyngées superficielles et urogénitales, en particulier chez les personnes immunodéprimées, notamment les personnes âgées et les victimes du SIDA.
« Un diagnostic précoce est essentiel pour une prise en charge rapide et efficace des patients ». (Directives de l’OMS sur les procédures opératoires normalisées pour le diagnostic en laboratoire des infections opportunistes du VIH)
Bien que C. albicans reste la principale espèce en cause, d’autres types, notamment C. tropicalis, C. krusei ou C. glabrata ont augmenté proportionnellement à mesure que de nouveaux agents antifongiques sont venus très efficacement à bout de C. albicans. Ceci est la preuve qu’une détection précise est essentielle pour un bon choix de traitement antifongique.
Application :
CHROMagar™ Candida est un milieu de culture chromogène sélectif destiné à être utilisé dans la détection qualitative directe, la différenciation et l'identification présomptive des espèces de Candida. Le test est réalisé à partir d’écouvillons de peau, de gorge, d'oreilles et d'échantillons vaginaux ainsi que des échantillons de crachats, d'urine et de selles, parallèlement à des cultures sur gélose de Sabouraud, pour aider au diagnostic de la candidose. Les résultats peuvent être interprétés après 20-48 h d'incubation en aérobie à 35-37 °C.
D'autres tests microbiologiques ou un typage épidémiologique sont nécessaires. Un manque de croissance ou l'absence de colonies sur CHROMagar™ Candida n'exclut pas la présence de Candida. CHROMagar™ Candida n'est pas destiné à diagnostiquer une infection, ni à guider, ni surveiller le traitement des infections.
1. Contraste élevé : Une coloration intense des colonies aidant à différencier les espèces et les cultures pluri-microbiennes.
2. Rapide : Incubation de 20 à 48 h.
5. Moins de charge de travail : Avec les milieux traditionnels tels que le Sabouraud, l'identification des cultures pluri-microbienne est difficile, tandis que CHROMagar™ Candida, simplement par la couleur de la colonie, différencie instantanément les différentes espèces de Candida et aide à localiser leurs colonies dans les cultures pluri-microbiennes.
3. Vue globale : Vue globale de la population Candida avec la possibilité de détecter les espèces majeures mais aussi les populations mineures.
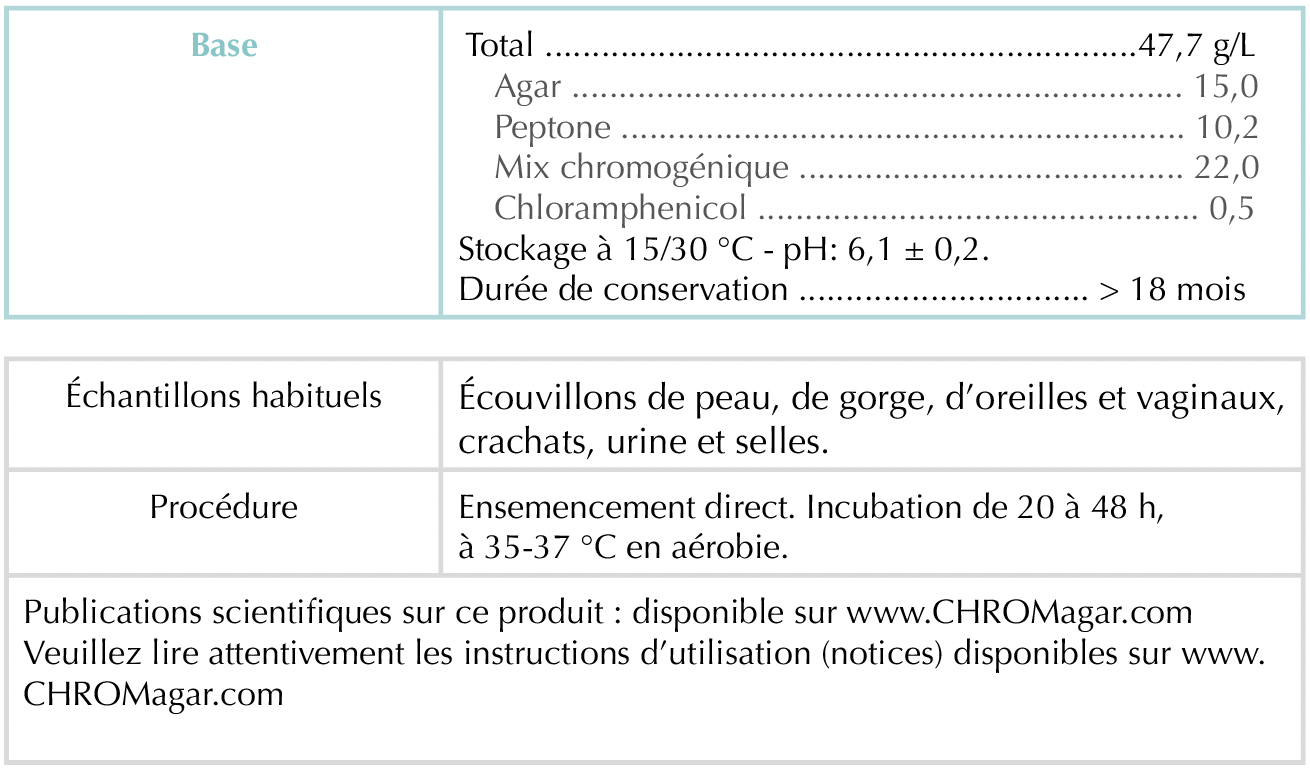
Composition
Documents techniques
Publications scientifiques
Thymoquinone Antifungal Activity against Candida glabrata Oral Isolates from Patients in Intensive Care Units—An In Vitro Study
Noura Nouri, Shahla Roudbar Mohammadi, Justin Beardsley, Peyman Aslani, Fatemeh Ghaffarifar, Maryam Roudbary and Célia Fortuna Rodrigues
Effect of Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy, using Toluidine blue ondual-species biofilms of Candida albicans and Candida krusei
Ana Beatriz Furtado Rodrigues, Juliene Cristina da Silva Passos, Maricilia Silva Costa
Identification of microorganisms grown on chromogenic media by MALDI-TOF MS
Petra Lüthje, Arthur B. Pranada, Duncan Carruthers-Lay, Marc Desjardins, Olivier Gaillot, David Warehame, Holly Ciesielczuk, Volkan Özenci
Fungal Spectrum and Susceptibility Against Nine Antifungal Agents in 525 Deep Fungal Infected Cases
Wenying Cai, Qianqian Ruan, Jiahao Li, Li Lin, Liyan Xi, Jiufeng Sun and Sha Lu
Identification of Candida Species Associated with Blood Infection by Multiplex PCR and Phenotypic Characteristics
Bahareh Fallah, Masoomeh Shams-Ghahfarokhi and Mohammadreza Salehi
Usefulness of Chromogenic Media with Fluconazole Supplementation for Presumptive Identification of Candida auris
Ruiz-Gaitán, A.; Sigona-Giangreco, I.; Pérez-Royo, J.M.; Garcia-Bustos, V.; García-Hita, M.; Valentín-Gómez, E.; Almaraz, S.G.; de Groot, P.W.J.; Pemán, J. Diagnostics 2023
Effects of Candidalysin Derived from Candida albicans on the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators in Human Gingival Fibroblasts
Nishikawa, Y.; Tomotake, Y.; Kawano, H.; Naruishi, K.; Kido, J.-i.; Hiroshima, Y.; Murakami, A.; Ichikawa, T.; Yumoto, H. Effects of Candidalysin Derived from Candida albicans on the Expression of Pro-Inflammatory Mediators in Human Gingival Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3256. https://doi.org/10.3390/ ijms24043256
Candida guilliermondii as an agent of postpartum subacute mastitis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: Case report
Tatiane Nobre Pinto, Alana Kohn, Gisela Lara da Costa, Laura M. A. Oliveira, Tatiana C. A. Pinto and Manoel M. E. Oliveira
Genomic landscape of blaGES-5- and blaGES-24-harboring Gram-negative bacteria from hospital wastewater: emergence of class 3 integron-associated blaGES-24 genes
Shino Takizawa, Eiji Soga, Wataru Hayashi, Kanae Sakaguchi, Shota Koide, Mizuki Tanabe, Tomohiro Denda, Yo Sugawara, Liansheng Yu, Shizuo Kayama, Motoyuki Sugai, Yukiko Nagano, Noriyuki Nagano.
Medically important Candida spp. identification: an era beyond traditional methods
EVREN, EBRU; GÖÇMEN, JULİDE SEDEF; İŞTAR, ELVAN HORTAÇ; YAVUZDEMİR, ŞÜKRAN; TEKELİ, FAZIL ALPER; YAVUZ, YASEMİN; and KARAHAN, ZEYNEP CEREN (2022) "Medically important Candida spp. identification: an era beyond traditional methods," Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences: Vol. 52: No. 3
Assessment of Identification Methods for Candida auris in Microbiology Laboratories in British Columbia
E.J. Eckbo et al. BC Centre for Desease Control
An in vitro study of isolation of candidal strains in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients undergoing radiation therapy and quantitative analysis of the various strains using CHROMagar
Mohammad Mohsin Abdul Razak Ainapur et Al. - General Dental Practitioner, Vijayapur, India
Prevalence of Candiduria in Diabetic Patients attending the Bafoussam Regional Hospital (West Cameroon) and Antifungal Susceptibility of the Isolates
Ngueguim D Aude, Iwewe Somo Y, Kechia F. Agem, Nangwat C, Diesse JM, Tchuenguem Tchuente R, Dzoyem JP
Identification of microorganisms grown on chromogenic media by MALDI-TOF MS
Petra Lüthje, Arthur B. Pranada, Duncan Carruthers-Lay, Marc Desjardins, Olivier Gaillot, David Wareham , Holly Ciesielczuk, Volkan Özenci
Evaluation of CHROMagar Candida in the rapid identification of medically important species of Candida
Lucilyn D. Lahoylahoy, Bernadette C. Mendoza. - Department of Biological Sciences, CSM, MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology, Iligan City. - The Institute of Biological Sciences, University of the Philippines-Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines
Evaluation of Candida species from Clinical specimens by using CHROMagar
Preeti Sharma, Sorabh Singh Sambyal and Divya Shrivastava International Journal of Advanced Research 5(2), 1750-1755 February 2017
Comparison of CHROMagar, polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism and polymerase chain reaction-fragment size for the identification of Candida species
Zahra Jafari, Marjan Motamedi, Nilufar Jalalizand, Gholam R. Shokoohi, Arezu Charsizadeh, Hossein Mirhendi Current medical Mycology December 2017
CHROMagar as a primary isolation medium for rapid identification of Candida and its role in mixed Candida infection in sputum samples
S. Mathavi, G. Sasikala, A. Kavitha, R. Indra Priyadarsini Indian J Microbiol Res 2016; 3(2) : 141-144
Evaluation of Diagnostic Efficacy of CHROMagar Candida for Differentiation and Identification of Common Candida Species
Ali Faraz , Usama Bin Ghaffar ,Tahir Ansari , Waqas Sami - College of Medicine, Majmaah University, Al-Majmaah, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Colonization and antifungals susceptibility patterns of Candida species isolated from hospitalized patients in ICUs and NICUs
Ali Zarei Mahmoudabadi A et al, Health Research Institute, Infectious and Tropical Diseases Research Centre, Ahvaz, Iran
Utility of Chromagar Medium for Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Candida Species Against Fluconazole and Voriconazole in Resource Constrained Settings
Shashir Wanjare, Rupali Suryawanshi, Arati Bhadade, Preeti Mehta
Routine identification and mixed species detection in 6,192 clinical yeast isolates
Carole Cassagne et Al. Laboratoire de Parasitologie-Mycologie, AP-HM, Marseille - France
Speciation of Candida species isolated from clinical specimens by using Chromagar and conventional methods
L. Sumitra Devi, Megha Maheshwari Department of Microbiology, SGT Medical College, Village Budhera, Haryana, India
Epidemiology, Antifungal Susceptibility and Pathogenicity of Candida africana Isolates from the United Kingdom
Andrew M. Borman, Adrien Szekely, Chistopher J. Linton, Michael D. Palmer, Phillipa Brown, Elizabeth M. Johnson Journal of Clinical Microbiology
Salivary Candida species carriage patterns and their relation to caries experience among Yemeni children
Nezar Noor Al-Hebshi, Eman Ahmed Al-Maswary, Zinab Othman Al-Hammadi, Nagwa Ghoname Departmet of Preventive Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, Jazan University; Jazan Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Evaluation of chromogenic media and seminested PCR in the identification of Candida species
Enas Daef, Ahmed Moharram, Salwa Seif Eldin, Nahla Elsherbiny, Mona Mohammed Medical Microbiology and Immunology Department, Faculty of Medecine, Assiut University, Assiut, Egypt. Botany Department, Faculty of Science, Assiut University, Egypt
Identification of Candida Species Screened from Catheter Using Patients with PCR-RFLP Method
Alireza Farasat 1, Mohammad Ghahri*1, Hossein Mirhendi 2 and Sedigheh Beiraghi 3 1 Biology Group, Basic Science Faculty, IHU University, Tehran, Iran 2 Mycology and Parasitology Medical Center, Health faculty and Health Research Institute, Tehran Medical University,
Comparación entre métodos convencionales, ChromAgar Candida® y el método de la PCR para la identificación de especies de Candida en aislamientos clínicos
a Instituto de Ciencias Biomédicas, Universidad Autónoma de Ciudad Juárez, Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, México b Departamento de Epidemiología, Hospital Regional de zona #6, Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social, Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, México Rev Iberoam Micol.
Characteristics of growth of yeasts and yeast-like fungi on chromogenic medium CHROMagar™ Candida (GRASO)
Katarzyna Goralska Department of Mycology, University of Warmia and Mazury, Poland
Do incubation temperature, incubation time and carbon dioxide affect the chromogenic properties of CHROMagar?
Dilek Yesim Metin, Husnu PULLUKCU, Suleyha HILMIOGLU POLAT, Ramazan INCI, Zekiye Emel TUMBAY Tubitak 2012, 42 (6) : 977-980
Evaluation of four chromogenic media for presumptive identification and differentiation of yeasts
M. Doluca Yucesoy et al., Izmir TR 2010, ECCMID Abstract from Clinical Microbiology and Infection. Volume 16 Supplement No.2, Page S666.
Use of CHROMagar Candida for the presumptive identification of Candida species directly from clinical specimens in resource-limited settings
Sayyada Ghufrana Nadeem et al. Libyan J Med 2010, 5 : 2144-DOI : 10.3402/ljm.v5i0.2144
Comparacion entre metodos convencionales, CHROMagar Candida y el método de la PCR para la idenfificacion de especies de Candida en aislamientos clinicos
D. Estrada-Barraza, A. Davalos Martinez, L. Flores-Padilla, R. Mendoza De Elias, L. Octavio Sanchez Vargas Revista Iberoamericana de Micologia 2010
Efficacy of Chromogenic Candida Agar for isolation and presumptive identification of pathogenic yeast species
E. Ghelardi et al. - Dipartimento di Patologia Sperimentale, Biotecnologie Mediche, Infettivologia ed Epidemiologia, Pisa, Italy
Sensibilidad a fluoconazol y voriconazol de aislamientos de Candida spp. obtenidos de mucosa oral de patientes con sida
Carolina Gutiérrez, Catalina De Bedout, Angela Maria Tobon, Luz Elena Cano, Myrtha Arango, Angela Maria Tabares, Angela Restrepo Infectio 2007; 11(4) 183-189
The evaluation of CHROMagar Candida as an isolation medium for identification of Candida species isolated from different clinical specimens
Berrin Ozcelik, Gazi University, Faculty of Pharmacy Turkey Turkish J. Pharm. Sci. 3 (1), 41-48, 2006
Candida Pseudorugosa sp. nov., a novel yeast species from sputum
Juan Li, Ying-Chun Xu and Feng-Yan Bai Journal of Clinical Microbiology December 2006
Evaluación del medio cromógeno CHROMagar CandidaTM para la identificación de levaduras de interés médico
Dres. Raquel Ballesté*, et al Departamento de Parasitología y Micología. Instituto de Higiene. Facultad de Medicina. Universidad de la República Rev Med Uruguay 2005; 21: 186-193
Polymicrobial candidaemia revealed by peripheral blood smear and chromogenic medium
H. Yera, D. Poulain, A. Lefebvre, D. Camus, B. Sendid J Clin Pathol 2004 ; 57 : 196-198
Evaluation of biochemical and serological methods to identify and clustering yeast cells of oral Candida species by CHROMagar test SDS-page and Elisa
Rodrigues J.A.O, Hofling J.F, Tavares F.C.A, Duarte K.M.R, Goncalves R.B and Azevedo R.A Braz. J. Biol., 64(2) 317-326, 2004
Detection of fluconazole-resistant isolates of Candida glabrata Detection of fluconazole-resistant isolates of Candida glabrata by using an agar screen assay
Nelson S. M. et al. 2003. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 41 : 2141-2143.
Replacement of Candida albicans with Candida dubliniensis in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients with oropharyngeal candidiasis treated with fluconazole
Martinez M., Patterson T. et al.2002. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 40 : 3135-3139.
Case report : Candida glabrata oropharyngeal candidiasis in patients receiving radiation treatment for head and neck cancer
Redding S. W. et al 2002. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 40 : 1879-1881.
Persistence of Pigment Production by yeast isolates grown on CHROMagar Candida medium
Duane R. Hospenthal, Clinton K. Murray, Miriam L. Beckius, Judith A. Green and David P. Dooley Journal of Clinical Microbiology December 2002, Vol. 40, No 12, p. 4768-4770
A Comparison of Methods for Yeast Identification Including CHROMagar Candida, Vitek System YBC and a Traditional Biochemical Method
Section of Clinical Microbiology, Division of Clinical Pathology, Department of Pathology, Tri-Service General Hospital; and Graduate Institute of Life Sciences, National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C. Chinese Medical Journal (Taipei) 2001;64:568-574
Simple, reliable, and cost-effective yeast identification scheme for the clinical laboratory
Koehler A. P. et al. 1999. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 37: 422-426.
Candida dubliniensis: An update
Sullivan D. J., D.C. Coleman et al. 1999. Rev. Iberoam Micol.,16 : 72-76.
Evaluation of CHROMagar Candida for rapid screening of clinical specimens for Candida species
Willinger B., Manafi M. 1999. Mycoses, 42 : 61-65.
Candida species from genital sites: their identification and susceptibility to fluconazole
Sim E. A. and Hughes C. 1998. British Journal of Biomedical Science, 55: 264-267.
Diferenciacion e identificacion presuntiva rapida de levaduras con el medio CHROMagar Candida
article in Spanish. Giusiano G. E. et al. 1998. Revista Argentina de Microbiologia, 30: 100-103.
An evaluation of the cost-effectiveness of using CHROMagar for yeast identification in a routine microbiology laboratory
Ainscough S. et al. 1998. J. Med. Microbiol., 47 : 623-628.
Detection of Candida dubliniensis in oropharyngeal samples from human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients in North America by primary CHROMagar Candida screening and susceptibility testing of isolates
Kirkpatrick W. R. et al. 1998. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 36 :3007-3012.
Identificacion de levaduras de interes clinico en el medio de cultivo CHROMagar Candida
Pedro Garcia Martos et al. Rev Iberoam Micol 1988; 15: 131-135
Appearance of colonies of Prototheca on CHROMagar Candida medium
Casal M. et al. 1997. Mycopathologia, 137 : 79-82
Molecular and phenotypic analysis of Candida dubliniensis : a recently identified species linked with oral candidosis in HIV-infected and AIDS patients
Coleman D. et al. 1997. Oral Diseases, 3 : 96-101.
Use of CHROMagar Candida for genital specimens in the diagnostic laboratory
Houang E.T.S. et al. 1997. Journal Clinical Pathology, 50 : 563-565.
Use of specialised isolation media for recognition and identification of Candida dubliniensis isolates from HIV-infected patients
Schoofs A., Odds F.C. et al. 1997. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.,16: 296-300.
Application of CHROMagar Candida for rapid screening of clinical specimens for Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida krusei, and Candida (Torulopsis) glabrata
Pfaller M.A. et al. 1996. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 34 : 58-61
Routine use of CHROMagar Candida medium for presumptive identification of Candida yeast species and detection of mixed fungal populations
Bouchara J.P. et al. 1996. Technical Report, 202-208.
Simple method for detecting fluconazole-resistant yeasts with chromogenic agar
Patterson T. et al. 1996. JCM, 34: 1794-1797.
Evaluation of a commercial medium for identification of Candida species
R. San-Millan, L. Ribacoba, J. Ponton, G. Quindos Journal of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 1996, Vol 15, No 2, pages 153-158
Use of CHROMagar Candida medium for isolation of yeasts from dental samples
Beighton D. et al. 1995. Journal of Clinical Microbiology,33:3025-3027.
CHROMagar Candida, a new differential isolation medium for the presumptive identification of clinically important Candida species
Odds F. et al. 1994, Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 32 : 1923-1929.